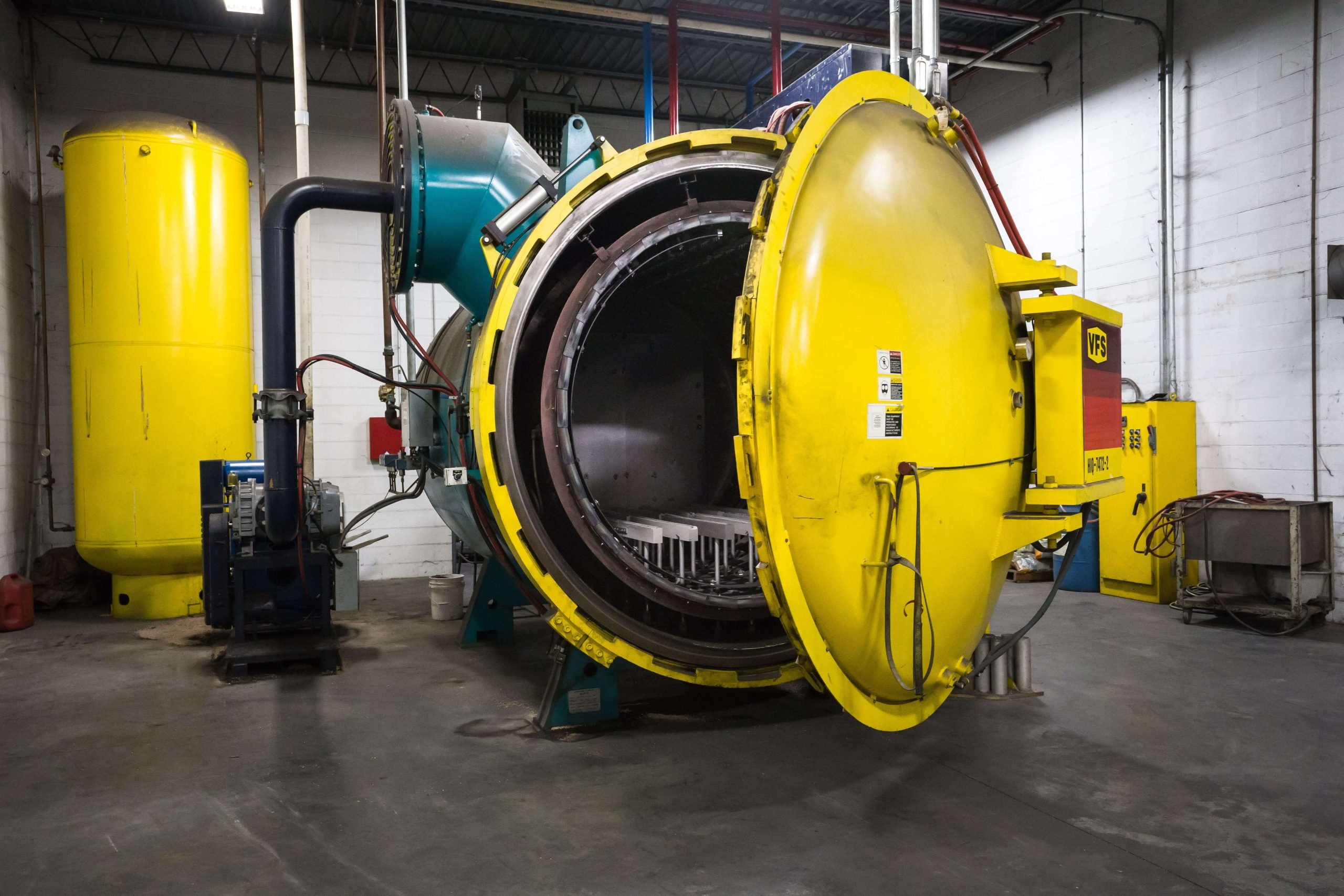
VACUUM HEAT TREATING CAPABILITIES
Many processes can be accomplished with the correct application of vacuum heat treatment, including:
- Normalizing
- Hardening
- Gas Fan Quenching
- Annealing
- Tempering
Explore each process below to discover which unique benefits they can provide for your chosen compatible base material.
VACUUM NORMALIZING
- Hardness and Strength: Vacuum normalizing imparts both hardness and strength to iron and steel parts.
- Stress Reduction/Relief: Reduces internal stresses induced by operations like forging, casting, machining, straightening, forming or welding. These stresses can lead to distortion or failure.
- Thermal Memory: Vacuum-normalized parts respond more consistently to lower-temperature processes thanks to thermal memory.
- Toughness Enhancement: Components requiring maximum toughness or those subjected to impact benefit from vacuum normalizing.
- Controlled Dimensional Changes: For large cross-sections (e.g., gear blanks), vacuum normalizing helps control dimensional changes during subsequent hardening or case hardening processes.
VACUUM HARDENING
- No Discoloration: In a vacuum, there aren’t any impurities that can cause the metal to get scalded or discolored.
- Avoid Oxidation: In a vacuumized environment, the absence of air prevents oxidation, preserving the metal’s surface finish while aging.
- Improved Properties: Vacuum hardening not only avoids damage but also enhances several material properties.
VACUUM GAS FAN QUENCHING (NITROGEN)
- Uniform Cooling: Gas quenching allows for uniform cooling of metal components, reducing distortion and minimizing deformities.
- Safety: Unlike liquid quenching, which can involve hazardous substances, gas quenching is safer and poses no risk of catching fire or releasing toxic waste.
- Environmental Friendliness: Gas quenching produces no toxic or combustible waste gas, making it more environmentally friendly than many liquid quenching methods.
- Austenitizing: As an early step in the quenching process, metal is heated in vacuum controlled conditions so its crystal structure can be changed.
VACUUM ANNEALING
- Avoid Intergranular Oxidation (IGO) and Surface Oxidation: In a vacuum, there is no exposure to air, preventing oxidation on the surface and between grain boundaries.
- Avoid Decarburized Areas: Vacuum annealing ensures that there are no de-carburized regions in the material, preserving its carbon content.
- Clean Surfaces of Parts After Heat Treatment: Vacuum annealing leaves parts with clean surfaces, eliminating the need for post-treatment washing.
VACUUM TEMPERING
- Eco-Friendly: Saves energy by reheating steel without excessive energy costs.
- Faster Process: Speeds up the job, allowing professionals to focus on other tasks.
- Avoid Discoloration: The reheating process occurs without discoloring the steel’s surface.
- Prevent Corrosion: Vacuum tempering imparts anti-corrosive qualities to the material, ensuring long-term rust-free performance.
- Clean Surfaces After Heat Treatment: Vacuum annealing leaves parts with clean surfaces, eliminating the need for post-treatment washing.
ACCEPTABLE BASE MATERIALS FOR VACUUM HEAT TREATING
Vacuum heat treating isn’t an ideal process for every metal, but it works well with the following materials:
- Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Titanium
- Inconel
- Kovar
- Copper
- Brass
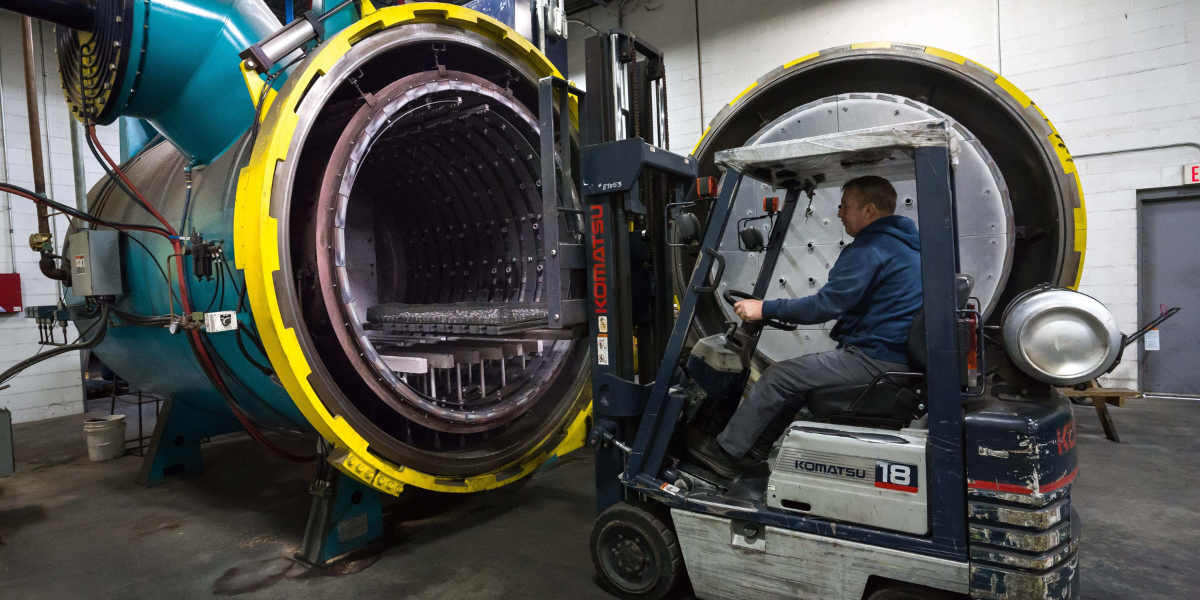

APPLICABLE INDUSTRIES
INCERTEC vacuum heat treatment services are used throughout a number of industries, including the following:
- Aerospace
- Military & Defense
- Medical Devices
- Automotive
- Oil & Gas
- Electronics
- Tooling